[2017.6 Digital Twin] Arduino - Communication
Arduino - Communication
Today I will continue study arduino. At first, I should figure out how to use the Arduino to contact with other device. I have seen, the Arduino IDE has a serial window. It just use the USB cable connect with computer. So I can Make an inference, that one the Arduino boeard, it includes already a USB-Serial chip. Arduino use it download program and also can use that to communicate.On the website, there are also 2 pins works als normal serial, pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX)
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Serial
So I can directly use UBS port to communicate with arduino!
Here are the function of the SERIAL
Serial.begin()
Serial.begin(speed)Serial.begin(speed, config)
speed: in bits per second (baud) - long rates: 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, or 115200.
config: sets data, parity, and stop bits. Valid values are :
SERIAL_8N1 (the default)
also there are serial1,serial2,serial3 but for arduino uno, there are only serial.
EG.
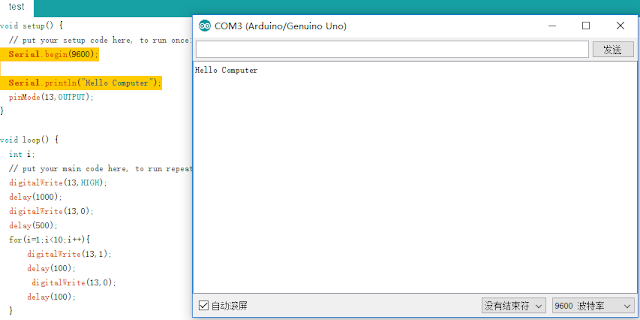
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Hello Computer");
end()
DescriptionDisables serial communication, allowing the RX and TX pins to be used for general input and output. To re-enable serial communication, call Serial.begin().
available()
DescriptionGet the number of bytes (characters) available for reading from the serial port. This is data that's already arrived and stored in the serial receive buffer (which holds 64 bytes). available() inherits from the Stream utility class.
void loop() {
// send data only when you receive data:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
incomingByte = Serial.read();
// say what you got:
Serial.print("I received: ");
Serial.println(incomingByte, DEC);
}
}
Reads incoming serial data. read() inherits from the Stream utility class.
// send data only when you receive data:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// read the incoming byte:
incomingByte = Serial.read();
// say what you got:
Serial.print("I received: ");
Serial.println(incomingByte, DEC);
}
}
read()
DescriptionReads incoming serial data. read() inherits from the Stream utility class.
by the way, the number from Serialavailable() will decrease by 1.
peek()
DescriptionReturns the next byte (character) of incoming serial data without removing it from the internal serial buffer. That is, successive calls to peek() will return the same character, as will the next call to read(). peek() inherits from the Streamutility class.
flush()
DescriptionWaits for the transmission of outgoing serial data to complete. (Prior to Arduino 1.0, this instead removed any buffered incoming serial data.)
print()
Serial.print(78) gives "78"
Serial.print(1.23456) gives "1.23"
Serial.print('N') gives "N"
Serial.print("Hello world.") gives "Hello world."
Serial.print(78, BIN) gives "1001110"
Serial.print(78, OCT) gives "116"
Serial.print(78, DEC) gives "78"
Serial.print(78, HEX) gives "4E"
Serial.println(1.23456, 0) gives "1"
Serial.println(1.23456, 2) gives "1.23"
Serial.println(1.23456, 4) gives "1.2346"
println() has a return at the end of line.
write()
DescriptionWrites binary data to the serial port. This data is sent as a byte or series of bytes; to send the characters representing the digits of a number use the print() function instead.
Serial.write(val)
Serial.write(str)
Serial.write(buf, len)
val: a value to send as a single byte
str: a string to send as a series of bytes
buf: an array to send as a series of bytes
len: the length of the buffer
serialEvent()
DescriptionCalled when data is available. Use Serial.read() to capture this data.





评论
发表评论